Bim package: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
[mesh] = msh2m_gmsh("fiume","scale",1,"clscale",.1); | [mesh] = msh2m_gmsh ("fiume","scale",1,"clscale",.1); | ||
[mesh] = bim2c_mesh_properties(mesh); | [mesh] = bim2c_mesh_properties (mesh); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
[[File:fiume_msh.png]] | [[File:fiume_msh.png]] | ||
<b> Set the coefficients for the problem:</b> | <b> Set the coefficients for the problem:</b> | ||
| Line 83: | Line 82: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
nelems = columns(mesh.t); | nelems = columns (mesh.t); | ||
nnodes = columns(mesh.p); | nnodes = columns (mesh.p); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 95: | Line 94: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
AdvDiff = bim2a_advection_diffusion(mesh, epsilon, 1, phi); | AdvDiff = bim2a_advection_diffusion (mesh, epsilon, 1, 1, phi); | ||
Mass = bim2a_reaction(mesh,delta,zeta); | Mass = bim2a_reaction (mesh,delta,zeta); | ||
b = bim2a_rhs(mesh,f,g); | b = bim2a_rhs (mesh,f,g); | ||
A = AdvDiff + Mass; | A = AdvDiff + Mass; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 103: | Line 102: | ||
<b> To Apply Boundary Conditions, partition LHS and RHS</b> | <b> To Apply Boundary Conditions, partition LHS and RHS</b> | ||
The tags of the sides are assigned by gmsh | The tags of the sides are assigned by gmsh we let <math> \Gamma_D </math> be composed by sides 1 and 2 | ||
and <math> \Gamma_D </math> be the rest of the boundary | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
GammaD = bim2c_unknowns_on_side(mesh, [1 2]); | GammaD = bim2c_unknowns_on_side (mesh, [1 2]); ## DIRICHLET NODES LIST | ||
GammaN = bim2c_unknowns_on_side(mesh, [3 4]); | GammaN = bim2c_unknowns_on_side (mesh, [3 4]); ## NEUMANN NODES LIST | ||
GammaN = setdiff (GammaN, GammaD); | |||
jn = zeros(length(GammaN),1); | |||
ud = 3*xu; | jn = zeros (length (GammaN),1); ## PRESCRIBED NEUMANN FLUXES | ||
ud = 3*xu; ## DIRICHLET DATUM | |||
Omega = setdiff (1:length (uin), union (GammaD, GammaN)); ## INTERIOR NODES LIST | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Add = A( | Add = A(GammaD, GammaD); | ||
Adn = A( | Adn = A(GammaD, GammaN); ## shoud be all zeros hopefully!! | ||
Adi = A( | Adi = A(GammaD, Omega); | ||
And = A( | And = A(GammaN, GammaD); ## shoud be all zeros hopefully!! | ||
Ann = A( | Ann = A(GammaN, GammaN); | ||
Ani = A( | Ani = A(GammaN, Omega); | ||
Aid = A(Ilist, | Aid = A(Ilist, GammaD); | ||
Ain = A(Ilist, | Ain = A(Ilist, GammaN); | ||
Aii = A(Ilist, | Aii = A(Ilist, Omega); | ||
bd = b( | bd = b(GammaD); | ||
bn = b( | bn = b(GammaN); | ||
bi = b( | bi = b(Omega); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 140: | Line 137: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
temp = [Ann Ani ; Ain Aii ] \ [ Fn+bn-And*ud ; bi-Aid*ud]; | temp = [Ann Ani ; Ain Aii ] \ [ Fn+bn-And*ud(GammaD) ; bi-Aid*ud(GammaD)]; | ||
u(Nlist) = temp(1:numel (GammaN)); | |||
u(Omega) = temp(length(un)+1:end); | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<b> Compute the fluxes through Dirichlet sides</b><br> | <b> Compute the fluxes through Dirichlet sides</b><br> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Fd = Add | Fd = [Add Adi Adn] * u([GammaD; Omega; GammaN]) - bd; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<B> Compute the gradient of the solution </B> | <B> Compute the gradient of the solution </B> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
[gx, gy] = bim2c_pde_gradient(mesh,u); | [gx, gy] = bim2c_pde_gradient (mesh, u); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<B> Compute the internal Advection-Diffusion flux</B> | <B> Compute the internal Advection-Diffusion flux</B> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
[jxglob,jyglob] = bim2c_global_flux(mesh,u, | [jxglob, jyglob] = bim2c_global_flux (mesh, u, epsilon, 1, phi); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<B> Save data for later visualization</B><BR> | <B> Save data for later visualization</B><BR> | ||
The resut can be exported to vtk format to visualize with [[http://www.paraview.org|paraview]] | |||
or [[https://wci.llnl.gov/codes/visit/|visit]] | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
fpl_vtk_write_field ("vtkdata", mesh, {}, {[gx; gy]', "Gradient"}, 1); | fpl_vtk_write_field ("vtkdata", mesh, {}, {[gx; gy]', "Gradient"}, 1); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 22:14, 19 July 2012
This is a short example on how to use bim to solve a DAR problem.
The data for this example can be found in the doc directory inside the
bim installation directory.
We want to solve the equation
with mixed Dirichlet / Neumann boundary conditions
Create the mesh and precompute the mesh properties
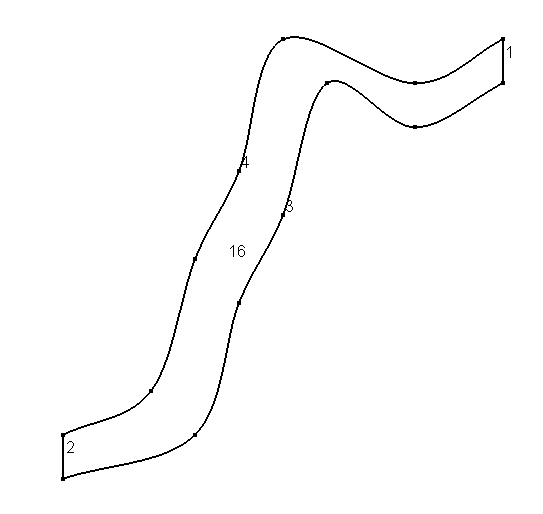
To define the geometry of the domain we can use gmsh.
the following gmsh input
Point (1) = {0, 0, 0, 0.1};
Point (2) = {1, 1, 0, 0.1};
Point (3) = {1, 0.9, 0, 0.1};
Point (4) = {0, 0.1, 0, 0.1};
Point (5) = {0.3,0.1,-0,0.1};
Point (6) = {0.4,0.4,-0,0.1};
Point (7) = {0.5,0.6,0,0.1};
Point (8) = {0.6,0.9,0,0.1};
Point (9) = {0.8,0.8,0,0.1};
Point (10) = {0.2,0.2,-0,0.1};
Point (11) = {0.3,0.5,0,0.1};
Point (12) = {0.4,0.7,0,0.1};
Point (13) = {0.5,1,0,0.1};
Point (14) = {0.8,0.9,0,0.1};
Line (1) = {3, 2};
Line (2) = {4, 1};
CatmullRom(3) = {1,5,6,7,8,9,3};
CatmullRom(4) = {4,10,11,12,13,14,2};
Line Loop(15) = {3,1,-4,2};
Plane Surface(16) = {15};
will produce the geometry below
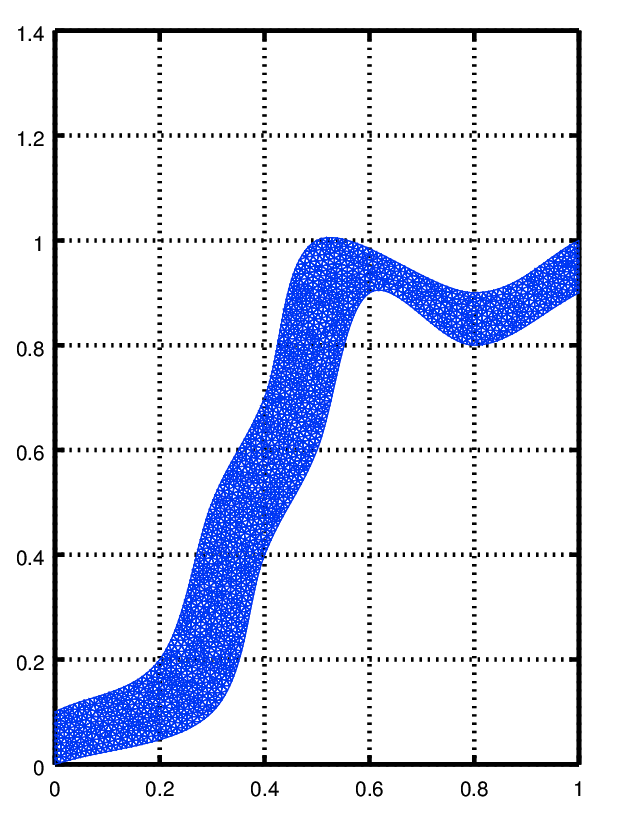
we need to load the mesh into Octave and precompute mesh properties check out the tutorial for the msh package for info on the mesh structure
[mesh] = msh2m_gmsh ("fiume","scale",1,"clscale",.1);
[mesh] = bim2c_mesh_properties (mesh);
to see the mesh you can use functions from the fpl package
pdemesh (mesh.p, mesh.e, mesh.t) view (2)
Set the coefficients for the problem:
Get the node coordinates from the mesh structure
xu = mesh.p(1,:).'; yu = mesh.p(2,:).';
Get the number of elements and nodes in the mesh
nelems = columns (mesh.t); nnodes = columns (mesh.p);
epsilon = .1; phi = xu + yu;
Construct the discretized operators
AdvDiff = bim2a_advection_diffusion (mesh, epsilon, 1, 1, phi); Mass = bim2a_reaction (mesh,delta,zeta); b = bim2a_rhs (mesh,f,g); A = AdvDiff + Mass;
To Apply Boundary Conditions, partition LHS and RHS
The tags of the sides are assigned by gmsh we let be composed by sides 1 and 2 and be the rest of the boundary
GammaD = bim2c_unknowns_on_side (mesh, [1 2]); ## DIRICHLET NODES LIST GammaN = bim2c_unknowns_on_side (mesh, [3 4]); ## NEUMANN NODES LIST GammaN = setdiff (GammaN, GammaD); jn = zeros (length (GammaN),1); ## PRESCRIBED NEUMANN FLUXES ud = 3*xu; ## DIRICHLET DATUM Omega = setdiff (1:length (uin), union (GammaD, GammaN)); ## INTERIOR NODES LIST
Add = A(GammaD, GammaD); Adn = A(GammaD, GammaN); ## shoud be all zeros hopefully!! Adi = A(GammaD, Omega); And = A(GammaN, GammaD); ## shoud be all zeros hopefully!! Ann = A(GammaN, GammaN); Ani = A(GammaN, Omega); Aid = A(Ilist, GammaD); Ain = A(Ilist, GammaN); Aii = A(Ilist, Omega); bd = b(GammaD); bn = b(GammaN); bi = b(Omega);
Solve for the displacements
temp = [Ann Ani ; Ain Aii ] \ [ Fn+bn-And*ud(GammaD) ; bi-Aid*ud(GammaD)]; u(Nlist) = temp(1:numel (GammaN)); u(Omega) = temp(length(un)+1:end);
Compute the fluxes through Dirichlet sides
Fd = [Add Adi Adn] * u([GammaD; Omega; GammaN]) - bd;
Compute the gradient of the solution
[gx, gy] = bim2c_pde_gradient (mesh, u);
Compute the internal Advection-Diffusion flux
[jxglob, jyglob] = bim2c_global_flux (mesh, u, epsilon, 1, phi);
Save data for later visualization
The resut can be exported to vtk format to visualize with [[1]] or [[2]]
fpl_vtk_write_field ("vtkdata", mesh, {}, {[gx; gy]', "Gradient"}, 1);